Two critical questions must be answered when considering double-cropped soybeans after wheat. Is there enough time for soybeans to reach maturity before a killing frost; and is there enough soil moisture left after wheat harvest? As the old adage goes for double-cropping, “If June is dry, do not try.”
Winter wheat crop development is currently ahead of normal, with estimates ranging from is about nine to 11 days ahead of normal based on growing degree day accumulations through May 20. That early harvest has many growers considering taking advantage of that larger window for double-cropping soybeans.

Table 1 shows current wheat growing degree day (GDD) accumulation through May 20, 2024.

The USDA’s Risk Management Agency expanded eligibility for federal crop insurance for double-crop soybean production following wheat in 58 counties in Michigan beginning in 2023 through a written agreement with no history of double-cropping (Fig. 1). Double-crop soybean yields range from 0 to 30 bushels per acre.
If there is not enough moisture near the surface to germinate the seed, critical time and yield potential will be lost. If the subsoil is dry, the soybeans will be entirely dependent on rainfall for the remainder of the season resulting in a risky venture. As the old adage goes for double-cropping, “If June is dry, do not try.”
Assuming adequate moisture is available, addressing the “enough time” question is multi-faceted and includes management decisions in several areas.
Wheat harvest timing
Although wheat is typically harvested at 13% to 15% moisture for sale or storage, grain yield and quality will not be decreased when harvesting at 20% to 22% moisture. The obvious advantage is in being able to plant seven to 10 days earlier.
A study in Kentucky found harvesting wheat at 20% to 22% followed by immediate soybean planting resulted in an 8–12 bu/ac soybean yield increase compared with harvesting wheat at 13% to 15% moisture.
Although glyphosate can be used as a pre-harvest aid in wheat, it is unlikely to significantly enhance wheat dry-down. The disadvantage of harvesting wheat early will be the added cost of drying or dockage.
Wheat straw
One approach to managing wheat residue is to cut wheat at 8–12” and ensure the combine distributes the chaff the entire width of the head. Growers can plant immediately following harvest with a no-till drill with discs that effectively cut through the residue down to planting depth.
This has the added advantage of conserving existing soil moisture by avoiding tillage. If available, using a stripper header will minimize residue on the ground. Taller wheat stubble will also help force soybeans to set pods higher off the ground, minimizing harvest losses due to missed pods.
Another approach is to cut and bale the straw prior to soybean planting. In addition to the extra revenue stream, the advantage here is in decreasing residue cover and increasing the chances of good seed-to-soil contact by avoiding “hair-pinning” of the straw in the furrow.
The disadvantage is the delay in getting soybeans planted, but if this operation can begin the same day as wheat harvest, the planting delay may be minimal.
Soybean planting
All of the same decisions that need to be made when planting soybeans in May need to be made when planting in July, with a few caveats. Conventional wisdom says plant by July 10 for a profitable crop although this is largely weather-dependent.
A rough rule of thumb is that 1 bu/ac/day is lost with delayed planting in July. With roughly 60 fewer days of the growing season ahead compared with a normal planting, changes must be made with respect to variety selection, seeding rate, row spacing, and more.
- Maturity group. Select a medium to long maturity group (see Fig. 2) to maximize yield. Selecting an ultra-early-maturing variety, although increasing the odds of reaching maturity before freezing, has consistently resulted in lower yields. However, a frost event prior to maturity will result in green plants at harvest. Ask your seed dealer about varieties that will yield well under double-crop.
- Stand count at harvest should be above 180,000, so aim for a seeding rate of 200,000 to 225,000.
- In order to quicken canopy closure and maximize sunlight capture, use as tigh
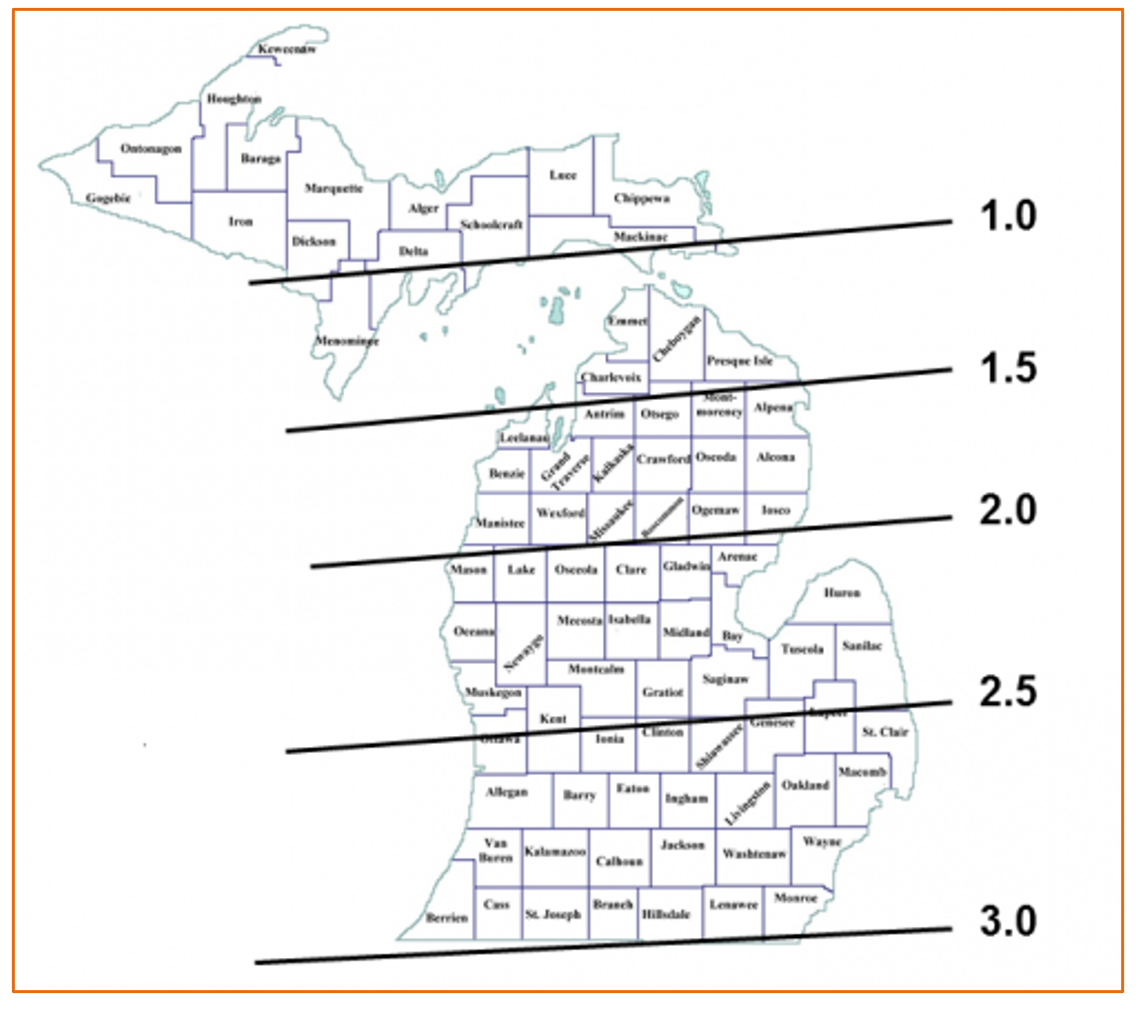
Figure 2: Soybean maturity zones in Michigan.
Weed control
Choose fields for double-cropping where weeds were adequately controlled with spring herbicide applications in wheat. However, be aware that some wheat herbicides have rotational restrictions for soybean (e.g., Huskie four months, Talinor 10 months).
Refer to Table 12 in the 2024 MSU Weed Control Guide for Field Crops for rotation restrictions for several common herbicides. Once wheat is harvested, weeds will typically grow rapidly as sunlight becomes more available. Depending on weed pressure and which species are present, these weeds may need to be controlled before soybean planting or emergence.
Volunteer wheat will also likely need to be controlled, so consider making a postemergence application after volunteer wheat has emerged and other weeds have outgrown injury from the wheat harvest. Remember, growing weeds (and volunteer wheat) will use up soil moisture, so timely control will be critical.
For those not planting a non-GMO soybean variety, selecting a herbicide-tolerant variety will provide more options for a double-crop weed control program. In-crop dicamba applications in Xtend soybeans are not allowed after June 30, so consider selecting Enlist E3, LibertyLink, or other traits besides Roundup Ready, particularly in fields with known glyphosate-resistant weeds.
For example, 2,4-D choline, glyphosate and glufosinate can be safely used on Enlist E3 soybean with no calendar date restriction. Do not use herbicides that will injure soybean (e.g., Cobra, Flexstar, Blazer) as yield will be impacted in this shorter-season crop.
Also consider including a residual herbicide to keep fields weed-free until canopy closure, particularly if later-emerging weeds like pigweeds or waterhemp are present.
Here are a few other considerations when considering double-crop soybeans following wheat.
- Select fields having few stones or consider rolling the fields after planting to reduce the potential for cutter bar damage when harvesting shorter plants.
- Avoid planting double-crop soybeans in fields infested with soybean cyst nematodes (SCN) as the shortened time between soybean crops will increase SCN populations.
- Scout for soybean aphids. If aphid populations are high in earlier-planted soybean, consider including an effective seed treatment (e.g. Gaucho, Cruiser) which would protect double-crop soybeans for 2-4 weeks as aphids move from earlier-planted fields to double-crop fields.
However, if aphids have reached threshold, a well-timed foliar application may provide more protection than a seed treatment. Aphids reproduce faster in late-planted soybeans and can cause more injury because the plants have less leaf area and root growth than soybeans planted earlier in the season.
Planting double-crop soybeans is risky in Michigan, but following the guidelines above can help reduce that risk. Also, be aware that this practice will add another soybean crop to your rotation. This can decrease future soybean yields by promoting higher levels of soil-borne diseases and soybean cyst nematodes.





